Dual effects of miR156-Targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana
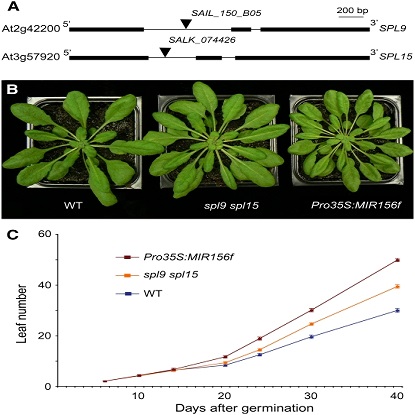
Full PDF link ABSTRACT Leaves of flowering plants are produced from the shoot apical meristem at regular intervals, with the time that elapses between the formation of two successive leaf primordia defining the plastochron. We have identified two genetic axes affecting plastochron length in Arabidopsis thaliana. One involves microRNA156 (miR156), which targets a series of SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) genes. In situ hybridization studies and misexpression experiments demonstrate that miR156 is a quantitative, rather than spatial, modulator of SPL expression in leaf primordia and that SPL activity nonautonomously inhibits initiation of new leaves at the shoot apical meristem.